Essential Hummingbird Nesting Practices for Success

Intro
Hummingbirds are exquisite creatures, captivating not just through their iridescent plumage but also through their unique nesting habits. Understanding hummingbird nesting practices is crucial for anyone interested in avian ecology or desiring to support these remarkable birds. Hummingbirds select specific nesting materials and locations, factors that are significant in ensuring their reproductive success. This article aims to explore these aspects while encouraging responsible stewardship of their environments.
As we embark on this exploration, it is essential to examine the intricacies that influence hummingbird nesting. From their behavioral traits to the environmental conditions required for nesting, each component plays a role in their reproductive cycle. This article passionately argues for the preservation and understanding of hummingbird habitats, integrating scientific insights with practical advice that can benefit both conservation efforts and biodiversity in local ecosystems.
Prologue to Hummingbird Nesting
Hummingbirds, known for their vibrant colors and remarkable abilities, play a crucial role in ecosystems. Understanding hummingbird nesting is essential for various reasons. It not only helps in the conservation of these birds but also contributes to the overall health of our ecological systems. This section focuses on the importance of nesting practices and highlights the ways in which successful breeding can be observed in these avian species.
Importance of Nesting in Avian Ecology
Nesting is a vital aspect of avian ecology. For hummingbirds, nesting means more than just finding a place to lay eggs; it is about creating a safe environment that supports the growth of their offspring. Nests provide protection from predators and harsh weather. The choice of nesting site can directly affect the survival rates of fledglings. Studies indicate that proper nesting practices can increase chick survival by providing adequate cover and resources.
Moreover, the success of hummingbird nesting contributes to the pollination of various plants. As they move between flowers, feeding on nectar, they facilitate the reproductive processes of plants. This interdependence highlights the importance of hummingbirds in maintaining biodiversity.
Overview of Hummingbird Species
Hummingbirds comprise a diverse group of species; new research suggests that there are over 300 different types globally. Each species has unique nesting behaviors and preferences. For instance, the Ruby-throated Hummingbird typically nests in deciduous forests, while Anna's Hummingbird is often found in urbanized environments.
The nesting habits vary significantly. Some species create elaborate nests using natural materials, while others rely on simpler structures. Understanding the particular needs of various species can help in creating optimal conditions for nesting.
In summary, an overview of hummingbird species reveals a rich tapestry of behaviors and ecological roles. Recognizing these nuances fosters a deeper appreciation for their biology and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Understanding Hummingbird Behavior
Understanding the behavior of hummingbirds plays a crucial role in comprehending their nesting practices. Hummingbirds exhibit distinct behaviors that affect their choices around mating, nest building, and overall nesting success. By knowing how these birds act in their natural environments, we can appreciate the intricacies of their reproductive processes and the ecological requirements for their nesting.
One fundamental aspect of their behavior is the mating rituals. These rituals can vary widely among species, and they influence not only the choice of mates but also the subsequent nesting practices. During courtship, male hummingbirds often display vivid colors and perform aerial displays to attract females. This behavior is not merely for show; it reflects the health and vitality of the males, indicating their fitness to produce healthy offspring.
Mating Rituals and Nest Selection
Mating rituals in hummingbirds are critical to the nesting process. Males participate in elaborate displays, which may include rapid dives and intricate flight patterns, showcasing their strength and agility. These displays help females select suitable partners. Once a female has made her choice, she typically assumes responsibility for nest construction.
The selection of a nesting site is heavily influenced by several factors, including availability of resources and protection from predators. Female hummingbirds often scout locations that offer hiding spots and close access to nectar sources. The ideal site allows for optimal convenience and security, thus enhancing the chicks’ chances of survival once they hatch.
Nesting Patterns Across Species
Hummingbird nesting patterns can vary significantly between species. For instance, the Ruby-throated Hummingbird often constructs its nests in deciduous trees, using materials like spider silk and plant fibers for support and insulation. In contrast, Anna’s Hummingbird prefers to build its nests in more open areas, often under eaves of buildings or branches of shrubs.
The choice of nesting materials reflects not only the availability in the environment but also an evolutionary adaptation to climate and predation pressures. By observing these patterns, conservationists and bird watchers can discern the specific needs of different hummingbird species. They can then tailor conservation efforts accordingly, aiming to create an environment that fosters successful breeding.
"Understanding nest construction and site selection among hummingbirds is essential for implementing effective conservation strategies. Different species require distinct habitats and resources to thrive."
In summary, recognizing the behaviors related to mating and nesting success gives us deeper insights into hummingbird ecology. It illustrates how species adapt to their environments and the critical components necessary for their survival.
Optimal Nesting Conditions
Understanding the optimal nesting conditions for hummingbirds is crucial for fostering successful breeding. These tiny birds have specific environmental needs that, if met, can lead to a higher success rate in nesting. Notably, these conditions influence not only where hummingbirds choose to build their nests but also their reproductive success. The right temperature and climate, along with managing potential threats from predators, create a safer space for raising the next generation.
Temperature and Climate Requirements
Hummingbirds thrive in a variety of climates but have preferences for certain temperature ranges. Generally, they favor warm conditions for nesting, as warmth facilitates metabolic functions essential for their activity. Ideal temperature varies by species, but many common species prefer daytime temperatures between 70°F to 90°F. During the nest-building phase, gentle weather patterns are also beneficial, as harsh winds or rain can damage fragile nests.


Moreover, different altitudes influence the microclimates available to them. For instance, species such as the Rufous Hummingbird can be found at higher elevations, where temperatures are cooler. Setting up their nests in protected, warm locations often leads to better breeding outcomes.
The climate should also provide accessibility to food sources. Hummingbirds require a steady supply of nectar from flowering plants, particularly during nesting season. This need offers insight into their preferred nesting sites, which are typically near abundant flowering species. To support these birds, it is essential to plant native flora that blooms during the nesting period.
Predator Management
Predator management is vital for enhancing the safety of hummingbird nests. Various predators, including snakes, cats, and larger birds, pose threats during the nesting period. A high nesting site, away from potential ground predators, is generally preferable. Additionally, selecting sites with dense foliage can offer further protection, as it conceals the nest from prying eyes.
Creating a layered habitat can also be effective. This includes planting shrubs and trees with varying heights around the nest area, which can deter predators by making it harder for them to navigate through the environment. Maintaining the area around a nesting site by removing potential hiding spots for predators can significantly improve nesting success.
It is important to remember that these conditions can be impacted by human activities. Urbanization or the use of pesticides can lead to increased predation or habitat loss. Therefore, creating a supportive environment requires awareness of these impacts and actively working against them.
"Enhancing predator management strategies is essential in creating a safe haven for hummingbirds during their most vulnerable time—the nesting period."
Materials Used in Nest Construction
Nest construction is a critical aspect of hummingbird survival and reproduction. The type and quality of materials used can significantly impact the success rate of nesting. To fully grasp the nuances of how hummingbirds select and utilize specific resources, we must consider both natural and artificial materials. Understanding these elements is essential for those looking to create better environments for these avian wonders.
Natural Resources for Nest Building
Hummingbirds are meticulous when it comes to selecting natural materials for their nests. They typically use items that blend seamlessly with their surroundings. Common materials include:
- Plant fibers: This can encompass hair, feathers, and the silky threads from plants like cotton or silk tree. These materials provide the necessary flexibility and structure crucial for nest integrity.
- Spider silk: Hummingbirds will often collect threads spun by spiders. This silk serves as an excellent adhesive, helping hold the nest components together.
- Moss and lichen: These materials provide insulation and create a camouflaged appearance, further protecting the nest from potential predators.
- Flower petals: Some species incorporate these for aesthetics, perhaps to attract mates or confuse other birds. Not only does this add beauty to the nest, it also can provide some protection against the elements.
The selection of these materials is not arbitrary. Hummingbirds choose items based on availability and the environmental conditions of their nesting sites. For instance, those in more temperate regions may rely heavily on moss, while others in arid climates may use more drought-resistant fibers.
Artificial Materials and Their Risks
While natural resources are ideal, in some scenarios, hummingbirds have been observed using artificial materials. This includes:
- Plastic fibers: Found in various forms, these are often used by hummingbirds when natural options are scarce. Although they may aid in nest building, plastic can lead to serious health risks for birds.
- Metal wire: Rarely, some hummingbirds might incorporate thin metal wire they find, which causes concern for the safety of hatchlings.
- Thread or yarn: These can also be appealing due to their texture, yet their use can create a hazardous environment if the thread becomes tangled around chicks or hinders movement.
The dangers associated with artificial materials are stark. Ingesting plastic or becoming entangled can lead to dire consequences, including injury or death. Therefore, while creativity in nesting behaviors can be beneficial from a resourcefulness perspective, it poses significant risks to the birds' well-being.
"Maintaining natural nesting environments is essential to reduce the reliance of hummingbirds on potentially harmful materials."
The End
Understanding what hummingbirds need for nesting allows for informed practices in habitat management. Encouraging the growth of native flora can help support hummingbirds by providing the necessary natural materials for their nests. In turn, this can foster a thriving population, adept at surviving the challenges posed by a changing world.
Recommended Nesting Locations
In the world of hummingbirds, the choice of nesting location plays a crucial role in their reproductive success. These locations affect not only the safety of the nest but also the ease of accessing food resources. Selecting appropriate habitats becomes essential for both hummingbird populations and enthusiasts looking to support their nesting practices. A clear understanding of the preferred habitats can provide insight into how to create corresponding environments.
Preferred Habitats of Hummingbirds
Hummingbirds thrive in varied environments. They adapt to landscapes that range from dense forests to more open areas like fields and gardens. However, certain specifics define their preferred habitats:
- Floral Diversity: Habitats with a rich variety of flowers are appealing. Hummingbirds utilize these for both nectar and nesting materials.
- Elevation: Many species prefer elevations that match their specific needs. Mountains or areas with hills can be attractive due to the abundance of preferred vegetation.
- Shelter from Predators: Nesting near shrubs, trees, or other structures that provide cover is vital. These locations offer safety from predators and harsh weather conditions.
- Access to Water: Proximity to water sources is important. Streams or ponds may provide hydration and foraging opportunities.
These elements contribute significantly to the success of nesting. Awareness of such factors allows for a better understanding of their natural behaviors and needs.
Creating Suitable Nesting Grounds in Your Yard


Creating suitable nesting grounds in one's yard involves several actions aimed at mimicking the natural habitats of hummingbirds. A few key steps can ensure hummingbirds find your yard appealing:
- Native Plants: Planting native species is essential. They attract hummingbirds and provide necessary nectar sources. Consider species like Bee Balm or Lantana.
- Nest Materials: Supply natural materials such as small twigs, spider silk, and mosses. These can assist in the construction of their nests.
- Avoid Pesticides: Limiting or eliminating chemical pesticide use can help maintain a thriving environment. Hummingbirds are sensitive to chemicals, and its presence can deter them.
- Provide Clean Water: Establish small feeders or a water feature. Constantly available water attracts hummingbirds for drinking and bathing, making your yard a suitable habitat.
"Nesting success for hummingbirds can be greatly enhanced through careful consideration of local flora and condition."
By integrating these practices into your yard, you create a welcoming atmosphere for these fascinating birds. The effort not only promotes their existence but enhances the ecological balance around you.
Human Impacts on Hummingbird Nesting
Understanding how human activities influence hummingbird nesting is crucial for preserving these small, vibrant birds. As nature's intricate systems face various challenges, recognizing the impact of urbanization, climate variations, and habitat destruction becomes essential. Such insights not only benefit conservation efforts but also raise awareness about the importance of creating harmonious relationships between humans and wildlife.
Urban Development and Habitat Loss
Urbanization is one of the profound threats to hummingbird nesting. Cities often expand into areas that were once rich habitats for these creatures. When forests and fields are turned into buildings or roads, hummingbirds lose both food sources and places for nesting. The fragmentation of habitats means birds have to travel longer distances to find suitable settings for raising their young, increasing their energy expenditure.
Moreover, urban environments are usually less hospitable due to the presence of artificial materials and pollutants. Pesticides commonly used in urban landscaping may contaminate nectar sources or harm the insects that hummingbirds rely on for protein. Such practices can lead to a decline in hummingbird populations, whose survival depends on healthy ecosystems.
Some effective strategies to mitigate these impacts include:
- Establishing Green Spaces: Encouraging the growth of parks and gardens using native plants can support local wildlife.
- Creating Wildlife Corridors: These can provide safe passage for birds between fragmented habitats.
- Promoting Community Education: Awareness initiatives can inform citizens about safe gardening practices that nurture hummingbirds.
Climate Change and Its Effects
Climate change presents another significant challenge for hummingbird nesting. As global temperatures rise, flower blooming patterns shift, disrupting the timing of food availability. Hummingbirds rely heavily on nectar from flowers, and variations in blooming can create food shortages when these birds need them most during breeding seasons.
Rising temperatures also contribute to habitat loss. Natural habitats may become unsuitable for specific hummingbird species that depend on particular climates. This may force them to relocate, further stressing populations already impacted by urban settings. Moreover, extreme weather conditions, like severe storms or droughts, can destroy nests and reduce chick survival rates.
To address the challenges posed by climate change, it is essential to:
- Monitor Climate Impact: Research on how climate factors affect hummingbird populations can inform conservation strategies.
- Encourage Adaptation: Efforts to plant diverse flora that can withstand climate variations are necessary. It helps ensure a steady food supply and nesting areas.
- Support Carbon Reduction Initiatives: Engaging in and advocating for environmental policies that limit carbon emissions can mitigate climate disruptions.
"Awareness of the interconnectedness of human activities and hummingbird nesting success is vital for sustainable conservation efforts."
These issues remind us that while enjoying the beauty of hummingbirds, we carry a responsibility to protect their habitats. By approaching urban development thoughtfully and acknowledging the signs of climate change, we can play a part in ensuring that these extraordinary creatures thrive.
Techniques for Supporting Hummingbird Nesting
Supporting hummingbird nesting involves practical actions that can create favorable conditions for these birds during their breeding period. Given the ecological challenges that hummingbirds face, it is crucial to implement techniques that enhance their habitat. These practices not only benefit the birds but also contribute to the overall health of local ecosystems.
Planting Native Flora for Food and Shelter
One significant way to support hummingbird nesting is through the planting of native flora. Native plants are adapted to the local environment and offer beneficial resources that non-native species may not provide. They serve as crucial sources of nectar and pollen for hummingbirds during the breeding season. For example, species like Salvia, Echinacea, and Monarda are attractive options that draw these birds in due to their vibrant colors and abundant nectar.
Additionally, native plants provide shelter and safe nesting sites for hummingbirds. Dense shrubs and trees can offer protection from predators and harsh weather conditions. When selecting plants, consider the local ecosystem's requirements to enhance biodiversity and create a rich habitat.
To establish a suitable area for nesting, it is advised to plant in clusters rather than solitary plants. Clusters mimick natural growth patterns and create a more inviting environment for hummingbirds.
Providing Safe Water Sources
Having access to clean water is essential for hummingbirds. They utilize water not only for drinking but also for bathing and maintaining their plumage. Thus, providing safe water sources is vital in supporting their nesting habits.
A shallow birdbath can be an effective solution, allowing hummingbirds to safely perch and enjoy the water without drowning risks. Ensure that any water source is consistently clean and refreshed. Adding rocks or pebbles in the birdbath can create landing spots, making it easier for the birds to access water without trouble.
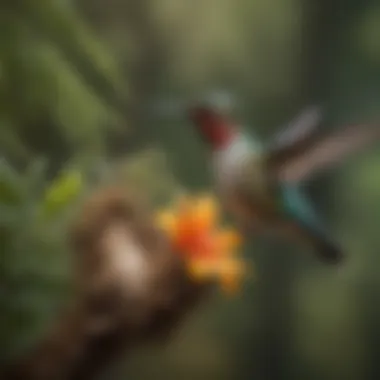

Also, consider incorporating a small fountain or dripper. The sound of flowing water can attract hummingbirds, encouraging them to visit. Just like with food sources, the availability of water must align with the overall safety and comfort of the nesting area.
"Supporting hummingbird nesting requires thoughtful planning. The establishment of native flora and safe water sources profoundly impacts the avian community and the surrounding ecosystem."
Monitoring Hummingbird Nests
Monitoring hummingbird nests is a crucial aspect of understanding and supporting these delicate birds and their nesting habits. By observing nests, researchers and enthusiasts can gain valuable insights into the behavior, health, and survival of hummingbirds. This practice contributes to the broader understanding of avian ecology and offers opportunities for citizen involvement in scientific endeavors.
Monitoring nests serves several significant purposes. Firstly, it aids in the assessment of nesting success, allowing us to determine which factors promote or hinder successful breeding. This can include identifying potential threats from predators or adverse weather conditions. Moreover, understanding the breeding habits of different species of hummingbirds helps in conservation efforts, guiding the protection and restoration of their habitats.
Secondly, nest monitoring also plays an educational role. It engages the public and raises awareness about the needs and behaviors of these birds. Encouraging responsible observation can lead to greater appreciation and stewardship of natural environments, encouraging individuals to take action to support hummingbirds in their neighborhoods.
Best Practices for Observing Nests
To effectively monitor hummingbird nests, specific best practices should be followed to ensure minimal disturbance to the birds. These practices include:
- Distance: Maintain a safe distance from the nest. Getting too close can stress the birds and lead to abandonment.
- Timing: Observe the nests during the early morning or late afternoon when hummingbirds are less active and more likely to be away from the nests.
- Stealth: Move quietly and avoid sudden movements to prevent alarming the birds.
- Recording Parameters: Take notes on date, time, weather conditions, and any other relevant observations without intruding on the nest environment.
- Use of Binoculars: Consider using binoculars or a camera with a zoom lens to observe without getting too close.
By adhering to these best practices, monitoring can be both productive and respectful of the natural behaviors of hummingbirds.
Citizen Science and Data Collection
Citizen science plays a vital role in the collective effort to understand and conserve hummingbirds. Engaging the public in monitoring nests contributes significantly to data collection efforts. Observations from various locations offer researchers a wider sample from which to analyze trends and patterns in hummingbird nesting behavior.
Participants in citizen science programs can contribute in various ways:
- Submitting Observations: They can report their observations through platforms such as iNaturalist or the Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
- Data Recording: Regularly noting the status of nests, including the number of eggs, hatchlings, and fledglings can help build a comprehensive picture of nesting success across species.
- Education Initiatives: Participating individuals can also educate others about hummingbird conservation and the importance of monitoring.
Collectively, these efforts yield valuable data that can inform conservation strategies and enhance understanding of the complex behaviors associated with hummingbird nesting.
Monitoring nests is not just an observation; it’s a step towards a deeper connection with our environment and its inhabitants.
Ending: Enhancing Hummingbird Nesting Environments
Enhancing hummingbird nesting environments is critical to the sustainability of these captivating birds. The earlier discussions in this article emphasize the nuances between various aspects of hummingbird nesting. These include their behavioral patterns, optimal conditions, and the impact of human activity. It is evident that achieving a balance between natural habitats and human presence is crucial for their continued survival.
To summarize, understanding best practices involves recognizing the specific needs of hummingbirds in terms of nesting materials, locations, and ecological conditions. By fostering suitable environments for nesting, we encourage not just population stability but also promote biodiversity. When we engage with nature by aligning with the nesting requirements of hummingbirds, we contribute to the broader ecosystem.
It’s also important to consider that every small effort counts. The contribution of planting native flora, managing predation risks, and providing safe water sources cannot be overstated. Each of these practices creates a layer of support for nesting hummingbirds, leading to more successful breeding.
"Creating environments that support hummingbird nesting is not merely about the birds. It reflects our responsibility toward preserving ecological balance."
By adopting best practices, we can make significant strides toward enhancing hummingbird nesting environments while also enjoying the beauty of these remarkable creatures.
Summarizing Best Practices
Summarizing the best practices for enhancing hummingbird nesting involves a combination of knowledge, action, and consistent care. Here are several key points to remember:
- Select native plants that provide both food and shelter. Species like bee balm, salvia, and trumpet creeper attract hummingbirds.
- Ensure a proper water supply, either through bird baths or natural features such as ponds. Clean water is never overlooked by nature.
- Manage predators effectively by creating cover and choosing nesting sites wisely. This boosts the chance of survival for the young.
- Monitor environmental changes. Changes due to climate can impact the success of nests. Stay informed to adapt practices accordingly.
- Educate others about the importance of hummingbird habitats. Collective action can lead to better community practices and results.
These practices, while seemingly simple, harness the power of awareness to drive meaningful change in how we approach hummingbird conservation.
Call to Action for Sustainable Practices
A call to action for sustainable practices emphasizes the importance of responsible engagement with our environment. The preservation of hummingbird nesting practices involves more than just local initiatives; it requires a collective commitment to sustainability. People can take small steps in their gardens or communities, but it is vital to encourage broader change.
Here are some steps you can take:
- Get involved in local conservation efforts to protect natural habitats.
- Support initiatives that protect native plants and discourage invasive species.
- Participate in citizen science projects focused on avian research and monitoring.
- Advocate for policies that prioritize ecological sustainability in urban planning.
- Share knowledge and resources with others to raise awareness about hummingbirds’ needs and issues.
By approaching hummingbird conservation with a proactive mindset, we can enhance their nesting environments effectively. Every action contributes to a future where these birds can thrive. Let us work together towards sustainable practices that benefit all aspects of our ecosystems.







